Stress-Strain Curve
Stress-Strain Curve: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Stress - Strain Graph, Proportion Limit, Elastic Limit, Yield Strength, Breaking Point in Elasticity, Elastic After-effect, Elastic Fatigue, Creep, Elastic Hysteresis, etc.
Important Questions on Stress-Strain Curve
Materials with stronger metallic bonds exhibit high malleability.
The ability of a material to undergo plastic deformation without rupture, when a compressive force is applied, is known as
Two wires of the same material and length but cross sectional area in the ratio are used to suspend the same loads. The extension in them will be in the ratio
Ultimate tensile strength of a metallic wire depends on its
Dimensional formula of modulus of elasticity is
What do you understand by the yield strength of a material?
A typical stress-strain curve for a wire of a metal wire is shown below:
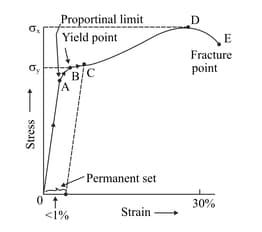
If the point D and E are very close, the material is:
The elastic behaviour of a body can be turned into plastic behaviour under the larger deforming force.
What do you understand by the plastic deformation of a body?
Permanent set refers to plastic strain in a material beyond _____ limit.
Permanent set in a material is produced by subjecting it to
Draw stressstrain curve for a metal and explain permanent set.
If diamonds are very hard then why are they so easily shattered when smashed with a sledgehammer?
